Choosing the Correct Auxiliary Verb in Italian
Italian has many compound tenses (verbs which are made up of two entities: auxiliaries + past participles). One of the most common compound tenses is the passato prossimo (the Italian equivalent of the past simple).
The auxiliaries used in compound tenses are either the verb avere or essere.
For example:
- Ho mangiato (I have eaten or I ate)
- Sono andato (I have gone or I went)
Textbooks (and teachers) say that transitive verbs (the verbs which trigger a direct object pronoun) use “avere” as an auxiliary, while intransitive verbs (the verbs which don’t trigger a direct object pronoun) use “essere”.
However, for language learners, determining whether a verb is transitive or not is not always straightforward and sometimes painful!
The rule I teach in my classes is different.
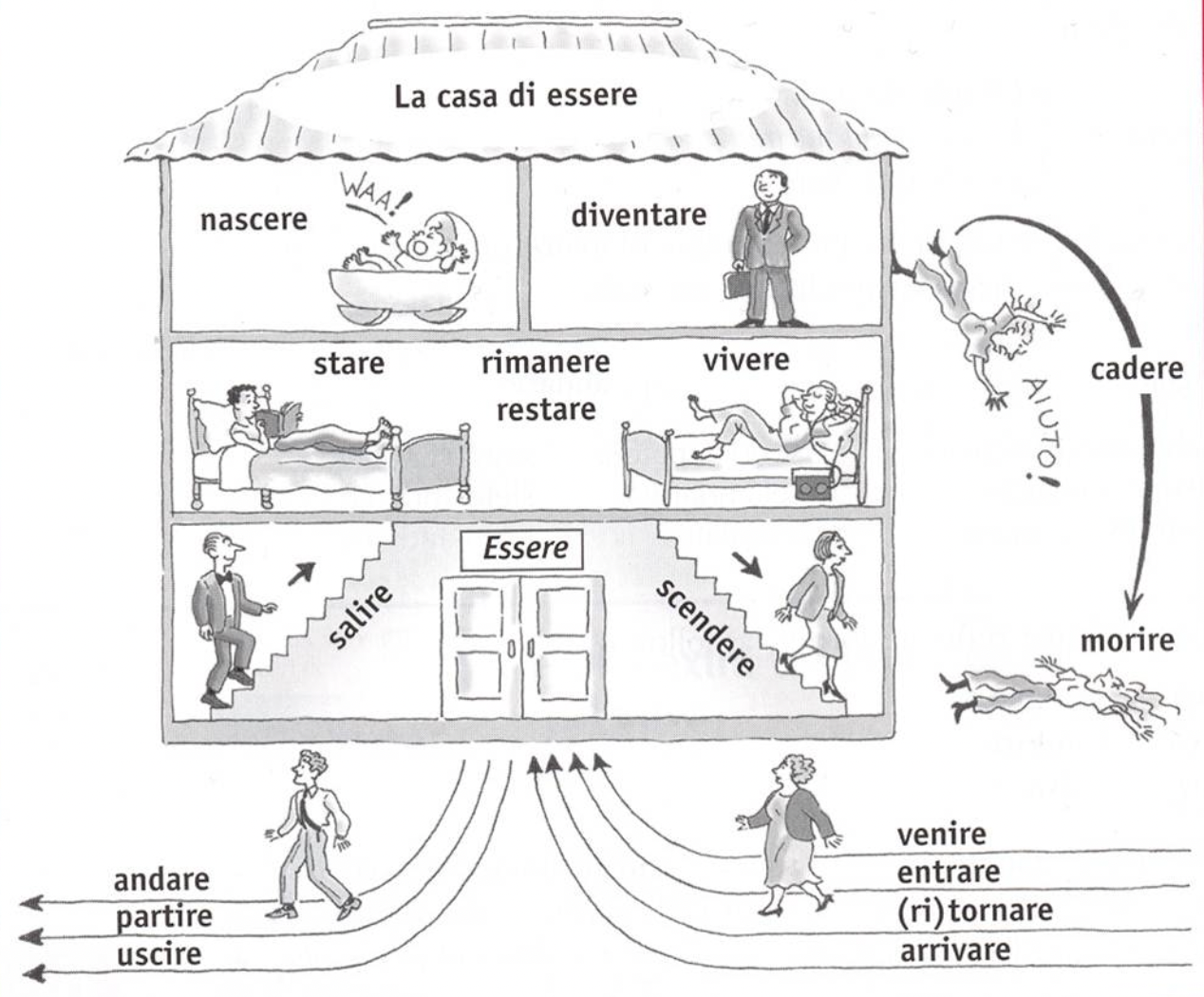
The list of essere verbs is actually very short and the best way to learn them is to memorize the so-called “casa di essere” (house of essere), which includes about a dozen high-frequency verbs.
Some grammar books (and teachers) will say that essere verbs are those that indicate motion or a change of state, which is partially true. Yet, some motion verbs like ‘camminare’ or ‘viaggiare’ won’t use “essere” as an auxiliary, even though they are intransitive. So, forget the whole motion/not motion verb logic and even the transitive/intransitive one. Instead, memorize la casa di essere.
My Tip:
Memorize ‘casa di essere’ instead of worrying about whether a verb is a motion verb or not, transitive or not. There aren’t many essere verbs in Italian. Memorizing the ten most common ones is the key to conjugating commands correctly and easily. And, by the way, the vast majority of verbs use “avere” as an auxiliary, so if in doubt, default to avere; you’re very likely, statistically, to be right.
List of “essere” verbs in Italian with the passato prossimo
| Infinitive Verb | Past Participle | English Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Andare | Sono andato/a | I went or I’ve gone |
| Partire | Sono partito/a | I left or I’ve left |
| Uscire | Sono uscito/a | I went out or I’ve gone out |
| Arrivare | Sono arrivato/a | I arrived or I’ve arrived |
| Venire | Sono venuto/a | I came or I’ve come |
| Entrare | Sono entrato/a | I entered or I’ve entered |
| Ritornare | Sono ritornato/a | I came back or I’ve come back |
| Tornare | Sono tornato/a | I came back or I’ve come back |
| Stare | Sono stato/a | I stayed or I’ve stayed |
| Rimanere | Sono rimasto/a | I remained or I’ve remained |
| Restare | Sono restato/a | I remained or I’ve remained |
| Scendere | Sono sceso/a | I went down or I’ve gone down |
| Salire | Sono salito/a | I went up or I’ve gone up |
| Diventare | Sono diventato/a | I became or I’ve become |
| Nascere | Sono nato/a | I was born |
| Cadere | Sono caduto/a | I fell or I’ve fallen |
| Morire | È morto/a | He/she died |
Test Your Italian
Not sure what your Italian level is? I’ve created a free online Italian test to help you determine it.How to Conjugate “Essere Verbs” in the Passato Prossimo
When using the passato prossimo with essere as a helping verb, the past participle of the main verb must agree in gender and number with the subject. This means that the endings of the past participle change to match the subject.
For example:
| Io | Sono andato/a | I have gone or I went |
| Tu | Sei andato/a | You have gone or you went |
| Lui/Lei | È andato/a | He/she has gone or he/she went |
| Noi | Siamo andati/e | We have gone or we went |
| Voi | Siete andati/e | You all have gone or you all went |
| Loro | Sono andati/e | They have gone or they went |
The Auxiliary of Reflexive Verbs
In Italian, reflexive verbs conjugated in the passato prossimo (present perfect) tense use the auxiliary verb “essere” (to be) instead of “avere” (to have) as the helping verb. This is a common rule in Italian grammar, and it means that the past participle of the reflexive verb agrees in gender and number with the subject of the sentence. For example:
| Io | Mi | Sono alzato/a | I got up |
| Tu | Ti | Sei alzato/a | You got up |
| Lui/Lei | Si | È alzato/a | He/she got up |
| Noi | Ci | Siamo alzati/e | We got up |
| Voi | Vi | Vi siete alzati/e | You all got up |
| Loro | Si | Si sono alzati/e | They all got up |








